
Architecture and features įront view of a Standard-A USB 3.0 connector, showing its front row of four pins for the USB 1.x/2.0 backward compatibility, and a second row of five pins for the new USB 3.0 connectivity. This gives USB 3.0 a potential total bidirectional bandwidth twenty times greater than USB 2.0.
#USB 2 VS USB 3 LOGO FULL#
USB 3.0 has transmission speeds of up to 5 Gbit/s, about ten times faster than USB 2.0 (0.48 Gbit/s) even without considering that USB 3.0 is full duplex whereas USB 2.0 is half duplex. Support for rotating media – the bulk protocol is updated with a new feature called Stream Protocol that allows a large number of logical streams within an Endpoint.Improved bus use – a new feature is added (using packets NRDY and ERDY) to let a device asynchronously notify the host of its readiness, with no need for polling.


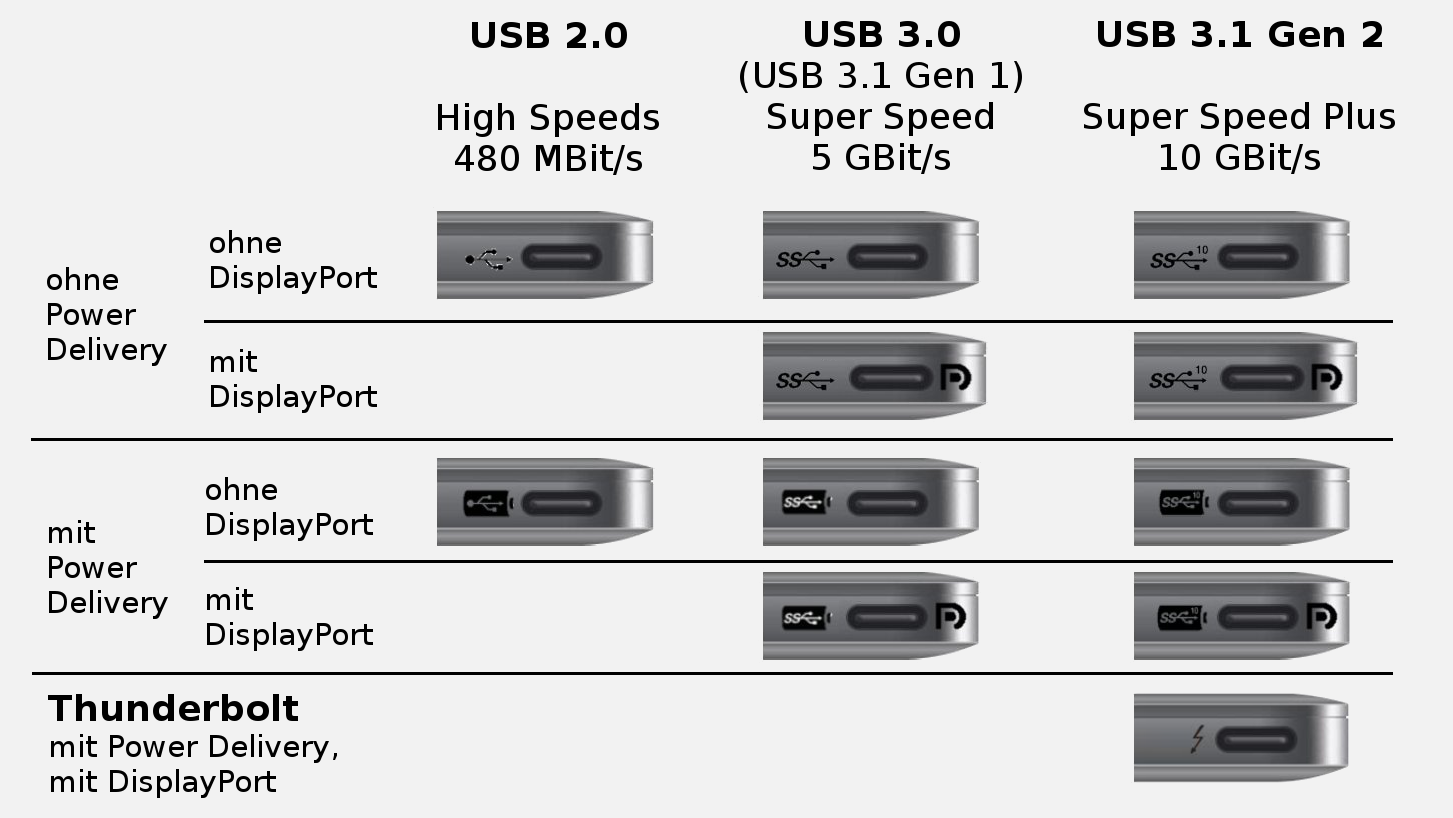
USB 3.2, released in September 2017, replaces the USB 3.1 standard. USB 3.1 preserves the existing SuperSpeed transfer rate, giving it the new label USB 3.1 Gen 1, while defining a new SuperSpeed+ transfer mode, called USB 3.1 Gen 2 which can transfer data at up to 10 Gbit/s over the existing USB3-type-A and USB-C connectors (1200 MB/s after encoding overhead, more than twice the rate of USB 3.0). USB 3.1, released in July 2013, is the successor standard that replaces the USB 3.0 standard. It is recommended that manufacturers distinguish USB 3.0 connectors from their USB 2.0 counterparts by using blue color for the Standard-A receptacles and plugs, and by the initials SS. Among other improvements, USB 3.0 adds the new transfer rate referred to as SuperSpeed USB (SS) that can transfer data at up to 5 Gbit/s (500 MB/s after encoding overhead), which is about 10 times faster than Hi-Speed (maximum for USB 2.0 standard).
#USB 2 VS USB 3 LOGO SERIAL#
USB 3.0, released in November 2008, is the third major version of the Universal Serial Bus (USB) standard for interfacing computers and electronic devices.

USB 3.0 Promoter Group ( Hewlett-Packard, Intel, Microsoft, NEC, ST-Ericsson, and Texas Instruments) ġ2 mm (A plug), 8 mm (B plug), 12.2 mm (Micro-A & Micro-B plugs)Ĥ.5 mm (A plug), 10.44 mm (B plug), 1.8 mm (Micro-A & Micro-B plugs)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
